Our Pipeline.
The start in our effort to change the way we treat cancer.
OxyLo’s HypoxyCaps Platform
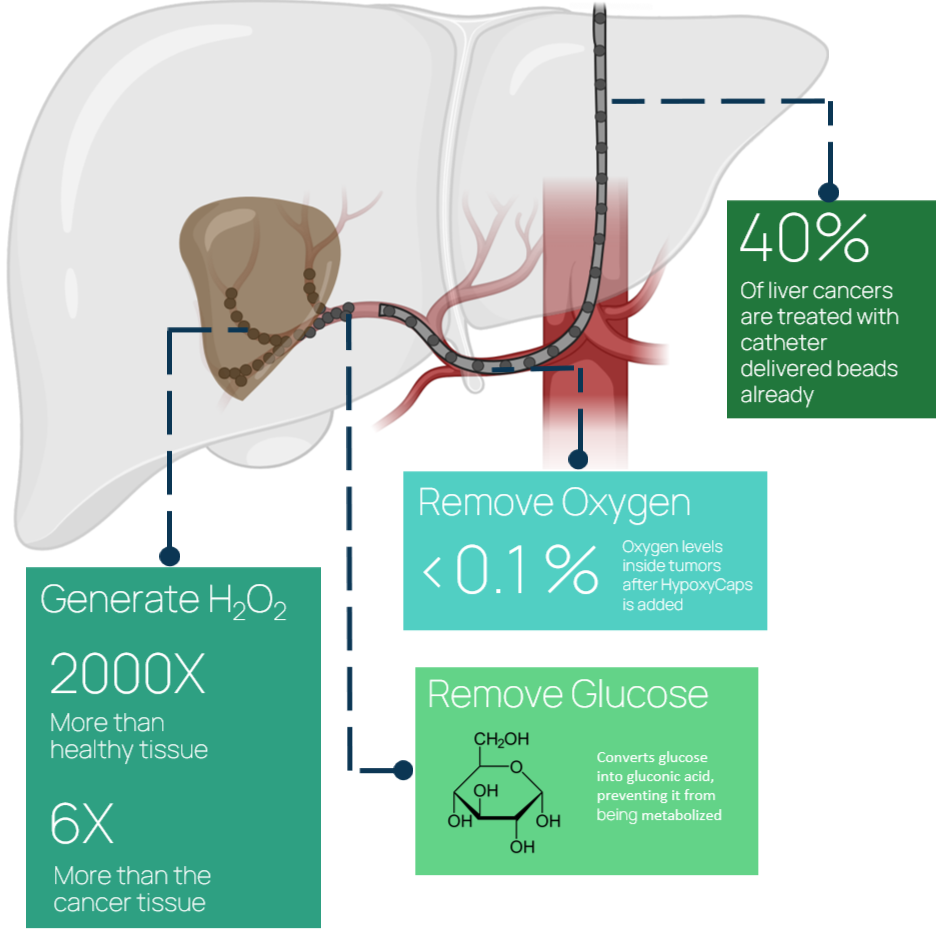
Many solid tumors become inoperable because of their depth, location, or the risk that surgery poses to the patient. In these cases—such as late-stage liver cancer—standard chemotherapy and radiation rarely shrink the mass enough to improve survival.
HypoxyCaps® tackle this unmet need. Powered by glucose, our enzyme-loaded micro-capsules strip the tumor of both oxygen and glucose within minutes of injection. A patented formulation locks unprecedented amounts of enzyme inside each biodegradable bead, ensuring potent, yet transient, activity with materials that are safe for patients and the environment.
Conventional embolic beads already treat roughly 40 % of liver-cancer cases, but they work only by blocking blood flow. By adding metabolic starvation, HypoxyCaps expand the kill-zone, deepening tumor response and aiming for longer patient survival.
Learn more about our technology here: https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2217557120
Our pipeline
We begin with enzyme-free HypoxyCaps that act as next-generation embolic beads, selectively lodging inside tumor vessels to cut off blood flow and trigger nutrient deprivation.
Building on that vascular blockade, our lead assets incorporate enzymes that rapidly deplete glucose and oxygen in the blocked region, converting passive embolization into a powerful dual-action therapy.
Method of treatment
Liver tumors draw most of their nutrition from an unusually dense arterial network, making them prime targets for embolization therapy. By delivering HypoxyCaps® directly into these vessels, we first block the blood supply, depriving the cancer of incoming fuel. Each micro-capsule then goes further: packed with enzymes, it rapidly consumes any residual glucose and oxygen inside the blocked region, compounding starvation and amplifying tumor death. The result is a double hit of mechanical embolization plus metabolic shutdown, designed to collapse even the most vascular tumors with a single, minimally-invasive injection.
Learn more about how our science works here.